A digital twin is a digital representation of a physical asset, process or system. It is distinguished from any other digital model by its dynamic connection to the physical twin. A digital twin unlocks value by supporting improved decision making.
Digital twins are tools that enable us to go through the information value chain more efficiently – turning data into insights that enable improved decisions and provide better outcomes.
Digital twins should not be constrained by definitions. They can connect to a variety of assets, processes, and systems using a variety of technologies, data types, data collection methods, analysis models, visualisation techniques and intervention types. The composition of a digital twin is driven by its use case and the purpose it serves.
The degrees of digitisation and digitalisation may also vary. By not constraining digital twins to a specific definition, we look beyond the potential complexity and realise their true value.
Outside of the built environment digital twins are used in other sectors such as manufacturing, agriculture and the automotive industry. We recognise that each sector uses diverse digital twins in different ways and to a different scale.
Digital twins should be systems based, purpose-driven and outcome focused.
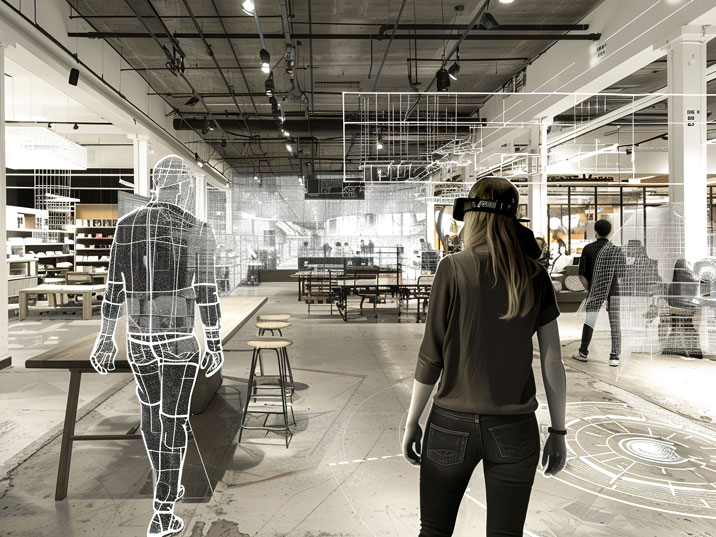

The Level 1 twin is a physically accurate realistic digital representation of an asset, facility, or product that emulates its real-world counterpart.
In summary, this serves as a highly accurate virtual model of a physical asset, emphasizing visual and physical representation over dynamic interaction or predictive functionalities.
Spatial awareness
Interaction
Experience
Collaboration
The Level 2 twin integrates real-time and right-time data to provide insights into the performance of an asset at specific points in time.
These, are tools to understand the complexities of interconnected systems and provide better insights to enable better decisions and interventions.
Real-time data
Monitoring and reporting
IoT
The Level 3 twin leverages data to predict the outcomes and problems for the operations of complex facilities and equipment.
In essence, This is a sophisticated tool that combines digital modelling with advanced analytical technologies to predict future states and optimize operational decisions.
Analytics
Decision-assist
Predictive maintenance
The Level 4 twin leverages advanced modeling and real-time simulation for potential future scenarios as well as prescriptive analytics and recommendations.
This is a highly advanced tool that not only anticipates the future but actively shapes it by offering specific recommendations and enabling informed decision-making.
What-if simulation
Machine learning
Intelligent recommendations
Process optimization
The Level 5 twin uses multiple real-time data feeds to learn and make decisions to correct issues automatically and enable predictive and prescriptive analytics.
This represents the integration of the most advanced aspects of IoT, AI, and analytics, functioning as a highly autonomous system
Autonomous action
Artificial Intelligence
The information value chain: showing the connection between data and better decisions that lead to better outcomes.
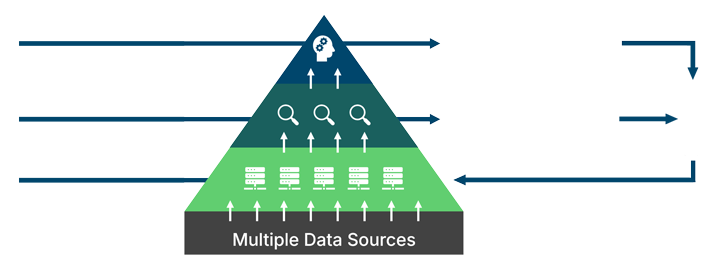
They connect diverse assets, processes, and systems using various technologies and data types, tailored to each use case and purpose. Unconstrained by rigid definitions, digital twins reveal their full potential across sectors like manufacturing, agriculture, and automotive, each applying them uniquely.
Effective digital twins are systems-based, purpose-driven, and outcome-focused.